- 0086-21-56469616
- 0086-18019205509
- minstar@minstargroup.com
- Language:English
- English
Your Location:Home >Products >Agrochemicals >137512-74-4
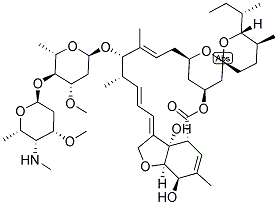

Appearance:White Crystalline Powder
Throughput:100|Kilogram|Month
pd_productuse:Intermediate
Delivery Time:large stock
Purity:99% purity
Emamectin benzoate Chemical Properties
Melting point 146-150°C
alpha D -6.9° (c = 0.5% in methanol)
vapor pressure 4 x 10-7mPa
storage temp. Refrigerator
pka 4.2; 7.6(at 25℃)
Water Solubility 320 mg l-1 (pH 5), 24 mg l-1 (pH 7), 0.1 mg l-1 (pH 9)
Safety Information
Toxicity LD50 in mallard ducks, northern bobwhite quail (mg/kg): 76, 264 orally (Chukwudebe)
MSDS Information
Emamectin benzoate Usage And Synthesis
Chemical Properties White Crystalline Powder
Uses A mixture of semi-synthetic Avermectins. Exists as the anhydrous and various hydrated forms having different crystal morphologies. Insecticide
Uses Insecticide.
Uses Emamectin benzoate is a second-generation avermectin insecticide highly effective against a broad range of lepidopteran larvae and certain other insects.
Metabolic pathway In laboratory studies, emamectin benzoate is relatively stable to aqueous hydrolysis (acid, neutral and alkaline) under dark conditions. Emamectin benzoate degrades extensively in soil via microbial action to multiple degradation products including the 8a-oxidation and 8a-hydroxylation products. CO2 and soil-bound residues were the major terminal residues which are incorporated into humic and fulvic acid fractions. In plants, emamectin benzoate degrades extensively to multiple polar components including the N-demethylated, N-formylated and conjugated products. Probably due to rapid elimination in faeces, the metabolic transformation of emamectin benzoate in animals is minimal. However, N-demethylation was observed as the major metabolic pathway. The hydrolytic, photolytic and overall metabolic pathways of emamectin benzoate in soils, plants and animals are presented in Schemes 1,2 and 3.
Degradation Emamectin benzoate (1) was relatively stable to hydrolysis in acidic, neutral and alkaline solutions (pH 5, 7 and 9) at 25 °C, with less than 10% degradation occurring after 30 days. It hydrolysed most rapidly in acidic solution (pH 5) at 25 °C with a DT50 of 136 days (Chukwudebe, 1992). Two polar components (each <10%) eluted close to the void volume under reversed phase chromatographic conditions.
The photodegradation half-lives of emamectin benzoate (10-12 mg 1-1) in buffered distilled water (pH 7) containing 1% (v/v) acetonitrile, ethanol or acetone as cosolvent under continuous exposure to a xenon lamp were 65,9 and 0.5 days, respectively. In both buffered and natural pond water, the major photodegradation products included 8,9-MAB1a (2), 8a-hydroxylated MAB1a (3) and minor unknown polar residues (Scheme 1). In sensitised buffered water, 8a-oxo-MAB1a (4) and 10,11-14,15-MAB1a diepoxide (5) were found as additional residual products (Mushtaq et al., 1997).
CAS:885523-08-0
CAS:517920-73-9
CAS:136735-95-0
CAS:3240-34-4